The next big thing in VR might not be higher resolution or more immersive sound, but an experience augmented by physical sensations or moving parts that fool your senses into mistaking virtual for reality. Researchers at SIGGRAPH, from Meta to international student groups, flaunted their latest attempts to make VR and AR more convincing.
The conference on computer graphics and associated domains is taking place this week in Los Angeles, and everyone from Meta to Epic to universities and movie studios were demonstrating their wares.
It’s the 50th SIGGRAPH, so a disproportionate amount of the event was dedicated to retrospectives and such like, though the expo hall was full of the latest VFX, virtual production, and motion capture hardware and software.
In the “emerging technologies” hall, or cave as the darkened, black-draped room felt, dozens of experimental approaches at the frontiers of VR seemed to describe the state of the art: visually impressive, but with immersion relying almost entirely on that. What could be done to make the illusion more complete? For many, the answer lies not in the virtual world with better sound or graphics, but in the physical one.
Meta’s varifocal VR headset shifts your perspective, literally
Meta was a large presence in the room, with its first demonstration of two experimental headsets, dubbed Butterscotch and Flamera. Flamera takes an interesting approach to “passthrough” video, but it’s Butterscotch’s “varifocal” approach that really changes things in the virtual world.
VR headsets generally comprise a pair of tiny, high-resolution displays fixed to a stack of lenses that make them appear to fill the wearer’s field of vision. This works fairly well, as anyone who has tried a recent headset can attest. But there’s a shortcoming in the simple fact that moving things closer doesn’t really allow you see them better. They remain at the same resolution, and while you might be able to make out a little more, it’s not like picking up an object and inspecting it closely in real life.
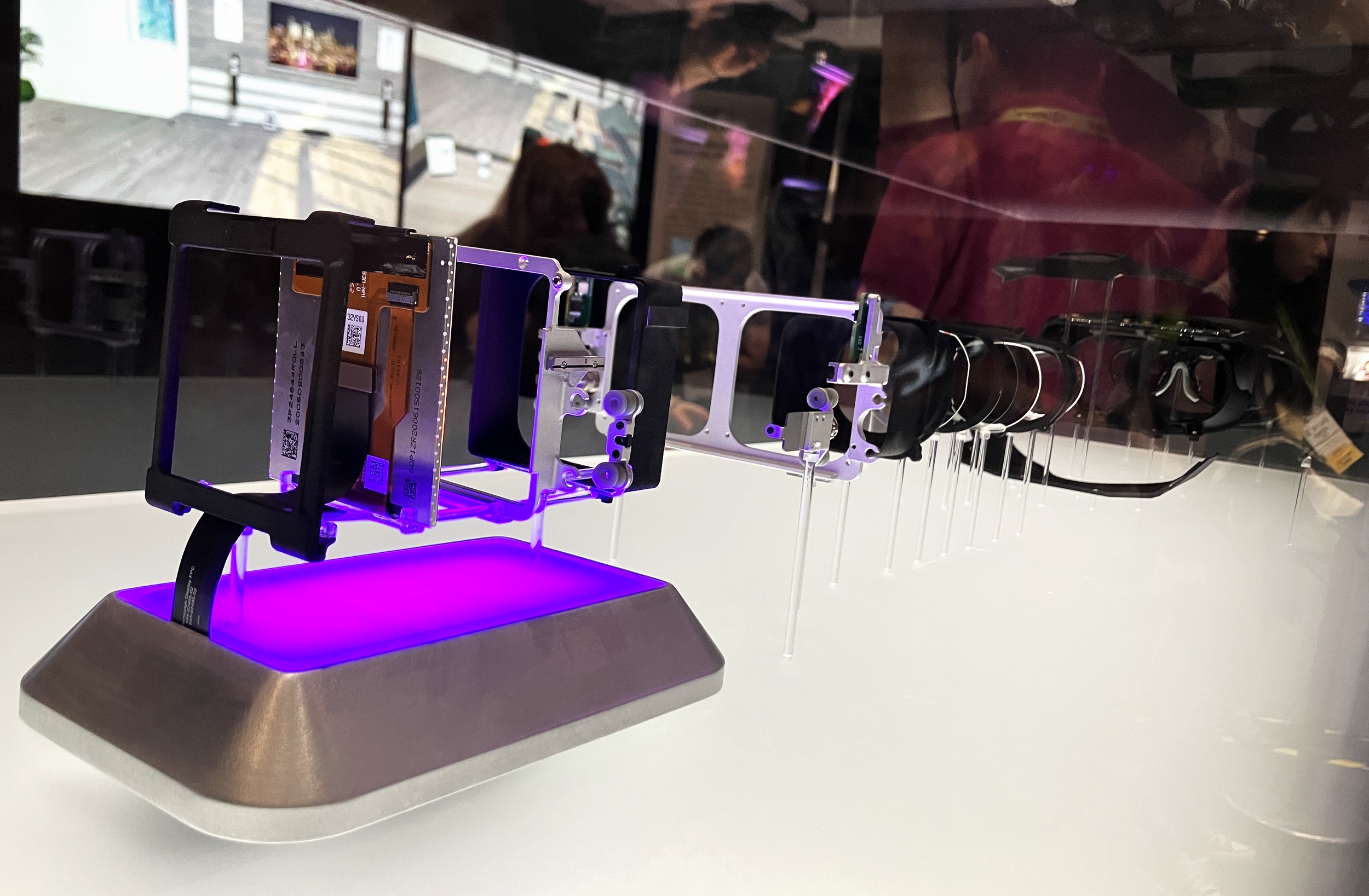

Meta’s Butterscotch prototype headset, in pieces.
Meta’s Butterscotch prototype, which I tested and grilled the researchers about, replicates that experience by tracking your gaze within the headset, and when your gaze falls on something closer, physically sliding the displays closer to your eyes. The result is shocking to anyone who has gotten used to the poor approximation of “looking up close” at something in VR.
The display only moves over a span of about 14 millimeters, a researcher at the Meta booth told me, and that’s more than enough at that range not just to create a clearer image of the up-close item — remarkably clear, I must say — but to allow the eyes to more naturally change their “accommodation” and “convergence,” the ways they naturally track and focus on objects.
While the process worked extremely well for me, it totally failed for one attendee (whom I suspect was a higher-up at Sony’s VR division, but his experience seemed genuine) who said that the optical approach was at odds with his own vision impairment, and turning the feature on actually made everything look worse. It’s an experiment, after all, and others I spoke to found it more compelling. Sadly the shifting displays may be somewhat impractical on a consumer model, making the feature quite unlikely to come to Quest any time soon.
Rumble (and tumble) packs
Elsewhere on the demo floor, others are testing far more outlandish physical methods of fooling your perception.
One from Sony researchers takes the concept of a rumble pack to extremes: a controller mounted to a sort of baton, inside which is a weight that can be driven up and down by motors to change the center of gravity or simulate motion.
In keeping with the other haptic experiments I tried, it doesn’t feel like much outside of the context of VR, but when paired with a visual stimulus it’s highly convincing. A rapid-fire set of demos first had me opening a virtual umbrella — not an game you would play for long, obviously, but an excellent way to show how a change in center of gravity can make a pretend item seem real. The motion of of the umbrella opening felt right, and then the weight (at its farthest limit) made it feel like the mass had indeed moved to the end of the handle.
Next, a second baton was affixed to the first in perpendicular fashion, forming a gun-like shape, and indeed the demo had me blasting aliens with a shotgun and pistol, each of which had a distinct “feel” due to how they programmed the weights to move and simulate recoil and reloading. Last, I used a virtual light saber on a nearby monster, which provided tactile feedback when the beam made contact. The researcher I spoke to said there are no plans to commercialize it, but that the response has been very positive and they are working on refinements and new applications.
An unusual and clever take on this idea of shifting weights was SomatoShift, on display at a booth from University of Tokyo researchers. There I was fitted with a powered wristband, on which two spinning gyros opposed one another, but could have their orientation changed in order to produce a force that either opposed or accelerated the movement of the hand.
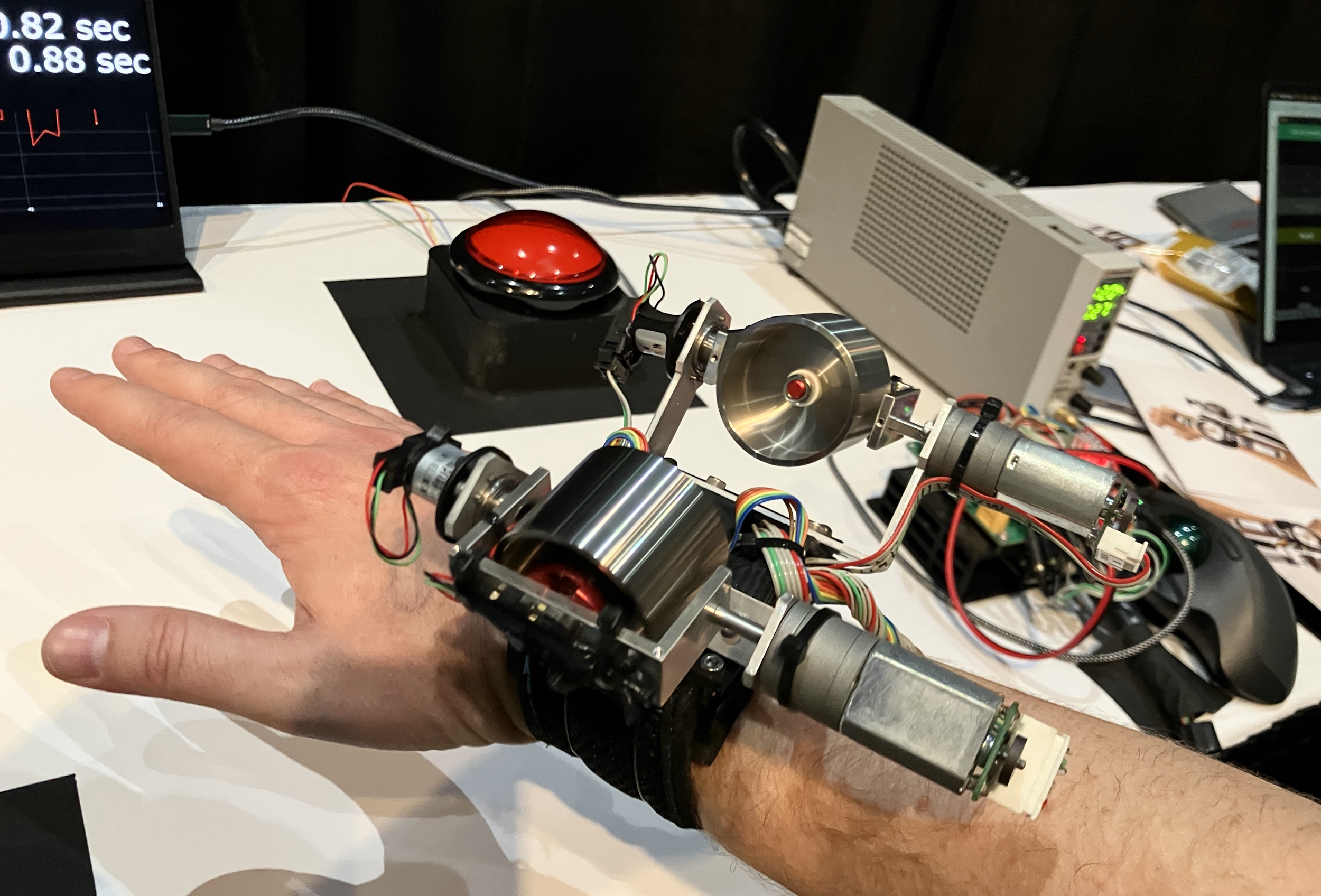
Image Credits: Devin Coldewey / TechCrunch
The mechanism is a bit hard to understand, but spinning weights like this essentially want to remain “upright” and by changing their orientation relative to gravity or the object on which they are mounted, that tendency to right themselves can produce quite precise force vectors. The technology has been used in satellites for decades, where they are known as “reaction wheels,” and the principle worked here as well, retarding or aiding my hand’s motions as it moved between two buttons. The forces involved are small but perceptible, and one can imagine clever usage of the gyros creating all manner of subtle but convincing pushes and pulls.
The concept was taken to a local extreme a few meters away at University of Chicago’s booth, where attendees were fitted with a large powered backpack with a motorized weight that could move up and down quickly. This was used to provide the illusion of a higher or lower jump, as by shifting the weight at the proper moment one seems to be lightened or accelerated upwards, or alternately pushed downwards — if a mistake in the associated jumping game is made.
Our colleagues at Engadget wrote up the particulars of the tech ahead of its debut last week.
While the bulky mechanism and narrow use case mark it like the others as a proof of concept, it shows that the perception of bodily motion, not just of an object or one appendage, can be affected by judicious use of force.
String theory
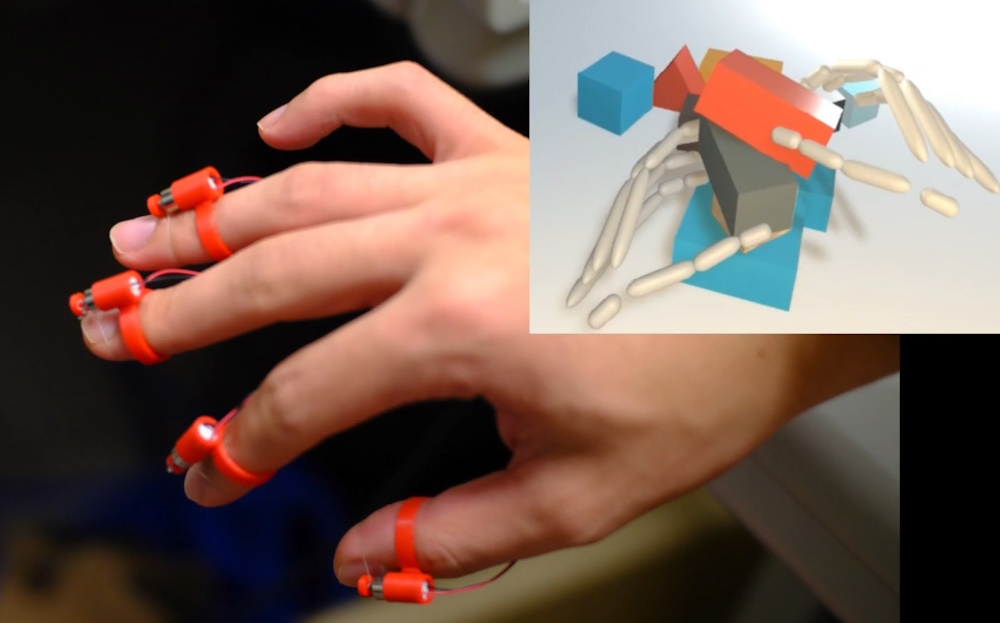
When it comes to the sensation of holding things, current VR controllers also fall short. While the motion tracking capabilities of the latest Quest and PlayStation VR2 headsets are nothing short of amazing, one never feels one truly interacting with the objects in a virtual environment. Tokyo Institute of Technology team created an ingenious — and hilariously fiddly — method of simulating the feeling of touching or holding an object with your fingertips.
The user is fitted with four tiny rings on each hand, one for each finger excepting the pinky. Each ring is fitted with a tiny little motor on top, and from each motor depends a tiny little loop of thread, which is fitted around the pad of each fingertip. The positions of the hands and fingers are tracked with a depth sensor attached (just barely) to the headset.
In a VR simulation, a tabletop is covered in a variety of cubes and other shapes. When the tracker detects that your virtual hand intersects with the edge of a virtual block, the motor spins a bit and tugs on the loop — which feels quite a lot like something touching the pads of your fingers!
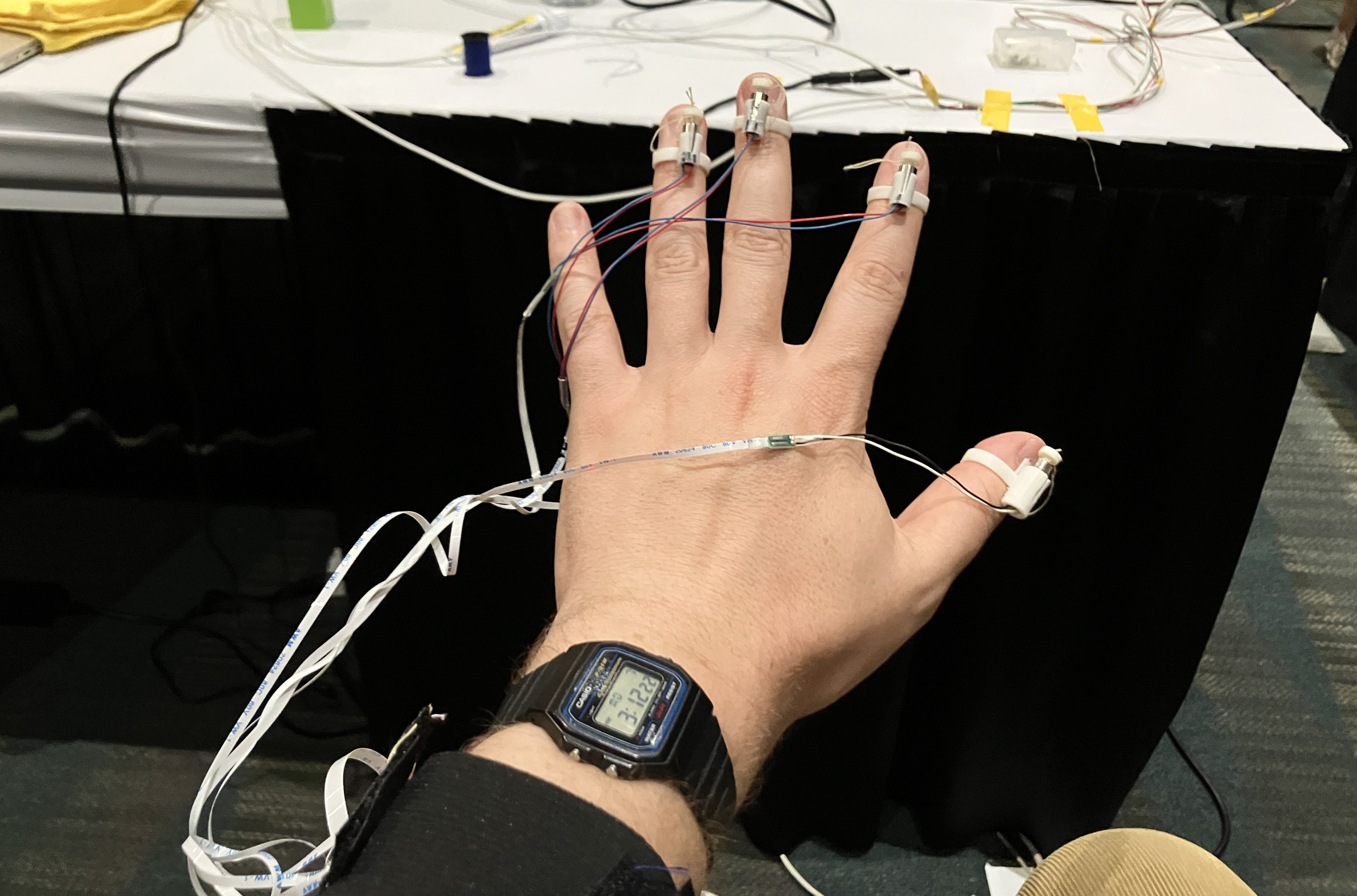
Image Credits: Devin Coldewey / TechCrunch
It all sounds very janky, and it definitely was — but the basic idea and sensation was worth experiencing and the setup was clearly not too expensive. Haptic gloves that can simulate resistance are few and far between, and quite complicated to boot (in fact another researcher present worked on this device, a more complex version of a similar principle). A refined version of this system might be made for under $100 and provide a basic experience that is still transformative.
SIGGRAPH and this hall in particular were full of these and more experiences that rode the line between the physical and digital. While VR has yet to take off in the mainstream, many have taken that to mean that they should redouble efforts to improve and expand it, rather than give it up as a dead platform.
The conference also showcased a great deal of overlap between gaming, VFX, art, virtual production, and numerous other domains — the brains behind these experiments and the more established products on the expo floor clearly feel that the industry is converging while diversifying, and a multi-modal, multi-medium, multi-sensory experience is the future.
But it isn’t inevitable — someone has to make it. So they’re getting to work.

