“We’re giving away money to strangers on the internet” is a pretty cavalier pitch for a new startup. But the more I learned about Placement, the smarter it sounded. In exchange for 10% of your income for 18 to 36 months, Placement will find you a much higher paying job, prep you for the interview and help you move to your new city of employment.
Actors, athletes and musicians have talent agents. Why shouldn’t office workers? That’s co-founder and CEO Sean Linehan’s vision for Placement. The former VP of product at Flexport thinks he can consistently get people a 30% raise on their cost of living-adjusted income if they’re willing to relocate from either their sleepy hometown or an overpriced metropolis.

“We think you can transform your life without becoming an engineer. You just have to be in the right place,” says Linehan. Not everyone is going to learn to code, and Placement isn’t a school. “We’re not in the business of training people to do jobs. We’re in training people to get jobs.”
Placement sits at the lucrative center of a slew of megatrends. People switching jobs more often. The desperate need to pay off crushing student loan debt. The rise of mid-size cities as rent gets out of control in San Francisco and New York. Social apps keeping people in touch from afar. The search for deeper fulfillment going mainstream.

Placement co-founder and CEO Sean Linehan
Through the normalization of income sharing agreements, Placement has found a way to powerfully monetize these societal shifts. That potential has attracted a $3 million seed round led by Founders Fund and backed by Coatue’s new seed fund, XYZ Ventures, The House Fund, plus angels like Flexport CEO Ryan Petersen, Eventbrite founders Julia and Kevin Hartz, DoorDash CEO Tony Xu, 137 Ventures MD Elizabeth Weil and her husband Facebook Calibra VP of Product Kevin.
With the cash to build out its jobseeker’s software toolkit, Placement could grow far beyond the Jerry Maguire-style boutique talent agency into a scalable way to put millions on a better career track. “The number one problem that I see in the American economy right now is the lack of income mobility,” Linehan says. “There are so many services for making rich people get richer, but what about services to help low-income people to get to the middle, or help those in the middle to improve?”
“If I stayed home, there’s just no way”
The CEO’s own rise was “a tried and true American tale,” he tells me. “I grew up in a pretty low-income neighborhood in San Bernardino . . . below the poverty line.” But a chance to attend UC Berkeley brought him to Silicon Valley, and the economic powerhouse city of San Francisco (before the housing crisis made it so expensive). “I don’t think I could have been as successful if I went to another place. If I had stayed in my home town, there’s just no way.”
Yet after college, when friends moved away and he broke up with his girlfriend, Linehan found himself living in a bunkbed by himself with extra space. “I called a friend back home working a minimum wage job, still living at home, and said ‘Your life kinda sucks. Come crash with me!,’ ” Linehan recalls. “He was super smart — smarter than most of the people I went to Berkeley with, but he never got on the train out of town.”
In the following years, Linehan coached his friend through becoming a professional and navigating interviews. “Now he’s tripled his income on a cost of living adjusted basis. He went from minimum wage to $70,000 to $80,000.” That ignited the idea for Placement. “How do you take that process of tapping people who are special and just need economic opportunity, and bring it to more people?” But Linehan needed a co-founder who could execute on getting these up-and-comers jobs.

That’s where Katie Kent came in. Also from the product team at Flexport, Kent had helped start Zipfian Academy as the first data science bootcamp in America. The 12-week crash course had been placing 93% of graduates into full-time roles when Zipfian was acquired by Galvanize, where Kent became director of outcomes with the mandate to get students great jobs. The right idea, experience and the track record of turning Flexport into a $3.2 billion freight forwarding unicorn led investors to jump at the chance to fund Placement.
Share me the money
So how exactly do Placement’s income sharing agreements work? “They only pay us if they make more money on a cost of living adjusted basis” Linehan explains.
First, the startup recruits through targeted advertising and word of mouth referrals, which the company says 100% of clients have provided. Primarily, it’s seeking business professionals with a skill mismatched to their city, such as sales, human resources or operations in a place without companies competing to hire for those roles. They might have never left their hometown or returned after school at a mid-tier college, suppressing their earning potential. But lack of knowledge about jobseeking, fears of leaving their support network or a lack of funds to finance a move keep them stuck there.

“There are two moments when society puts a gentle hand on your shoulder saying its okay to move away: when you go to college and when you graduate college,” says Linehan. “We’re trying to engineer a third moment. We give people the permission and space to have that conversation with their family by providing that forcing function.” Placement serves the same utility the CEO did for his friend, revealing that if they seize the opportunity of moving to a growing but still affordable city like Denver, Austin, Raleigh or Seattle, “people’s lives would be so much better.”
The other demographic Placement seeks is the 10 million-plus workers who’ve gotten in over their heads in some of the country’s priciest cities. “If you’re ambitious and talented but not an engineer in SF, this is a hard life. The costs are exceeding the benefits at this point.” Placement looks for cheaper cities where their skills are still relevant and they might even earn the same or a little less, but they can fetch a huge increase in income on a cost of living-adjusted basis and they have a path to buying a house. Linehan declares that “Our controversial opinion is that more important than reskilling people is getting them to the right place where the work is happening in the first place.”

Placement then evaluates the prospective client in what is currently an extremely selective process to determine if they’re undervalued based on their skills, qualifications, shortfalls and redflags. If they’re already being adequately or overpaid, it won’t accept them. Those eligible are offered access to Placement’s research on all the optimal salary and location/hirer pairs for their role, which most people wouldn’t or couldn’t do themselves. Linehan says, “We run their job search for them. We’re kind of like a concierge.”
Once they’ve selected some targets, Placement quarterbacks their preparation process, helping them to improve their LinkedIn and resume, practice telling their story and offering mock interviews with experts in their field. As they progress through interviews Placement sets up and requires hirers offer remotely, it teaches clients to negotiate to get their best possible compensation.
“If you’re a normal person who didn’t go to an elite institution or are a couple years out of school, there’s no resources,” Linehan laments. While some top coding schools and other bootcamps place graduates, and some startups like Pathrise are also working on interview prep, most seeking a new employer end up relying on mediocre job hunting tips they find online. That’s in part because it was hard to get people to fork over significant cash in exchange for instruction that wasn’t guaranteed to help.
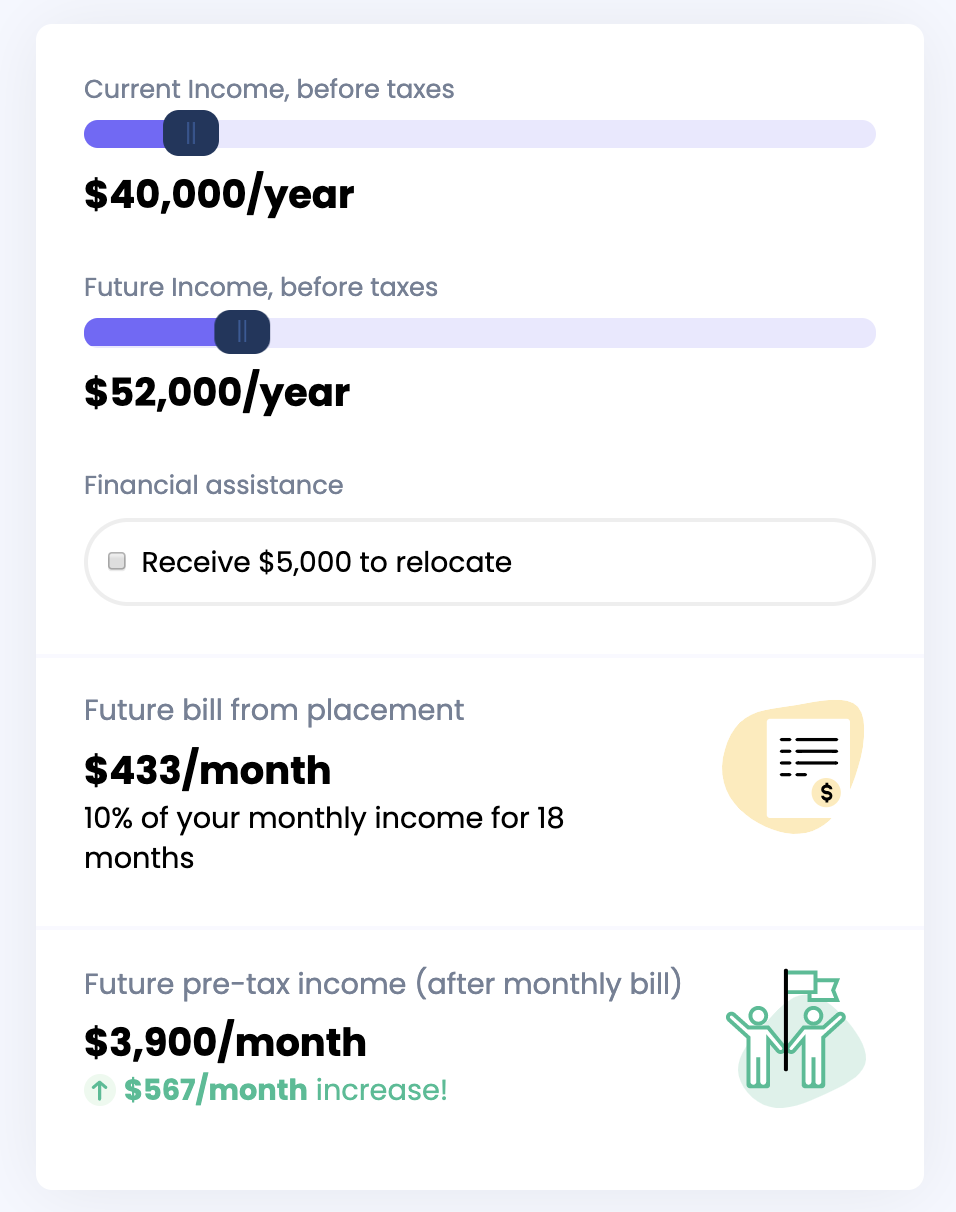
How Placement income sharing agreements work
The Placement income sharing agreement is designed to align incentives, though. It’s vested in getting clients not only the best job and salary, but one they’ll want to stick with. As long as the startup nets them a higher adjusted income, clients pay 10% of their earnings. That lasts for 18 months, or 36 months if they receive Placement’s $5,000 relocation stipend and human support. There are also caps on the total Placement can get paid back, and the agreement dissolves after five years so clients aren’t locked in if things don’t work out.
For example, Placement aims to help someone earning $40,000 per year pre-taxes reach $52,000 on a cost of living adjusted basis. They’d end up paying Placement $7,794 over the course of 18 months, or $433 per month. After the bill, they’d still be earning $3,900 per month, or $567 more than they used to. If they take the $5,000 relocation stipend and extra assistance, their ISA extends to 36 months and they’ll end up paying back $15,588 total, including the stipend.
Clients are likely to keep growing their compensation after their Placement ISA ends, so they’ll start reaping all the added proceeds. The startup has worked with fewer than 1,000 clients to date, but is supposedly growing quickly.
Eventually, Placement could move into working with programmers and designers, but it sees a big gap in assistance for business roles. Linehan notes that “We’re providing an option that will be available to a lot more people than a Lambda School or Galvanize coding bootcamp. Not everyone’s going to be software engineers.”
Making America anti-fragile
The biggest hurdle for Placement will be scaling what can be quite a hands-on, relationship-driven process of matching clients with the right hirers. “It’s one thing to get one person a job. It’s another to get 10,000 people a job,” Linehan admits. But he conquered the same problem at Flexport, which was moving 1,000 shipping containers across the ocean but had to figure out “how the hell do you move 1 million?”

Placement co-founders (from left): Katie Kent and Sean Linehan
That requires Placement to pour product know-how into building tools that equip clients to take more initiative to match themselves with hirers and teach themselves interview skills. It also must automate more of its marketing outreach, client screening and connections to recruiters while retaining a human element worth a four to five-figure price.
Right now, the startup’s team numbers just four, and though it will expand to seven soon, it may need to raise a bunch more to chase this dream. Some investors have been understandably skeptical about the whole “handing out $5,000” model without onerous ISAs.
For comparison, the one-year MissionU school for business and data jobs that was acquired and shut down by WeWork asked for 15% of income for three years without a relocation stipend, or $23,400 on a $52,000 per year job. ISAs for General Assembly’s tech job education cost 10% for 48 months, even if students don’t earn more than in their old job. Pathrise’s slimmer offering costs just 7% for one year. Colleges are jumping on the trend too, with some working with startup Leif to run their ISAs.
Placement has plans to cover prickly edge cases. If someone gets laid off from their new job, the startup will help them find another. “We’re on the hook to make sure they’re successful,” Linehan insists. It only won’t step in if an employee is fired for an ethical problem like sexual harassment or committing fraud. And if someone simply gets lonely in their unfamiliar city, they’re not required to stay, though moving home could hurt their earnings and Placement’s take. That’s why the startup is working to help its clients find community, even amongst each other, so they don’t feel isolated, and prefers sending workers to cities where they know someone.
Meanwhile, Placement must resist the temptation to become a hiring agency paid by employers and instead work fully on behalf of its clients. “When you’re aligned economically with the employer, you’re just chasing dollars from bigger and bigger whales of companies, and at one point you figure out you’re a recruiting firm for the Gap,” Linehan says with a shudder. The complexity of dealing with the U.S. Internal Revenue Service is enough hassle, so Placement doesn’t intend to work with jobseekers abroad or those that need visas, as “it’s not good for startups if you’re at the mercy of the government.”

Luckily, U.S. salaries total $8.6 trillion per year, Linehan claims, so it’s got enough of a domestic market. “The American economy is so huge that I don’t see other people tackling problems like that being competitive.” Placement does have potential to use its data to recommend and teach specific skills. “If you just make this change, if you learn Excel, you could totally get this job in a different industry that pays more and that you’ll like more,” Linehan says. He also dreams of one day improving urban planning by suggesting cities build music venues or parks that jobseekers say would soften the landing of moving there.
Zooming out, there’s also chance for Placement make the country more stable and resistant to strong-man populism promising financial security. “A two-tier society is fragile. I don’t want to live in a democracy where there’s a bunch of hay waiting for a matchstick to set it on fire,” Linehan concludes. “There doesn’t have to be a have and a have-not class, and you don’t need the government to do forced redistribituion to make everything fair. You just need people that care about getting on the right track, and that to me is a worthy cause to dedicate a life to.”



 Ready first joined PayPal in 2013 when it
Ready first joined PayPal in 2013 when it 
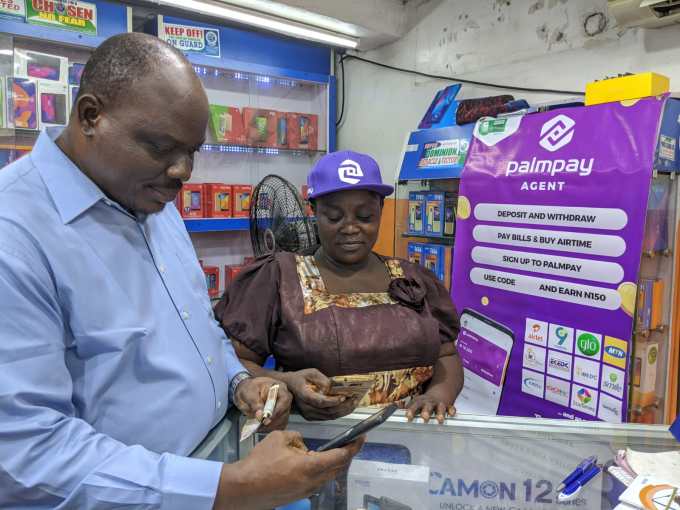




 To that end, PalmPay conveniently entered a strategic partnership with its lead investor. The startup’s payment app will come pre-installed on Transsion’s mobile device brands, such as Tecno, in Africa — for an estimated reach of 20 million phones in 2020.
To that end, PalmPay conveniently entered a strategic partnership with its lead investor. The startup’s payment app will come pre-installed on Transsion’s mobile device brands, such as Tecno, in Africa — for an estimated reach of 20 million phones in 2020.