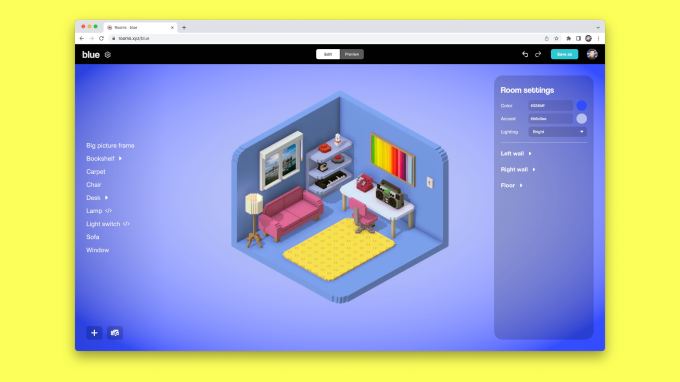
A team of ex-Googlers is today launching a new digital creativity platform, Rooms.xyz, into beta testing. The startup, backed by $10 million in seed funding led by a16z, offers a browser-based tool for designing 3D spaces — or “rooms” — using drag-and-drop, editable objects or code, allowing users to express themselves through creative play as they design rooms, basic games or other interactive activities contained in these small, online spaces.
The idea is something in between a simple creation tool like Minecraft and a more advanced world-building platform, like Roblox. Or, as the company describes it, it’s like the “digital equivalent of LEGO.”

Image Credits: Rooms.xyz
The idea for Rooms was inspired by a combination of factors, explains co-founder Jason Toff — namely, that 3D model creation today was far too difficult.
Prior to Rooms, Toff spent ten years at Google, off and on, in product marketing and product management, including at YouTube, Area 120, and in VR/AR. Before that, he spent a couple of years at Vine as Product Manager, including after it was acquired by Twitter. And most recently, Toff worked at Meta, where he dabbled with new product experiments, like the zine maker E.gg and music-making app Collab, among other things.
After leaving his last position, Toff decided to take some time off, which he decided to fill by trying to learn how to make 3D models — something he always thought sounded like fun. As it turned out, however, the process was actually fairly complicated and involved the use of complex software. Around the same time, Toff’s six-year-old son had just started playing with Minecraft where designing with 3D models was easy, but it had to be done one block at a time.
This prompted the idea of something of a middle ground for 3D design, where the process would be nearly as straightforward as it was in Minecraft, but the building unit wasn’t a single block. Instead, in Rooms, you can search for, edit, and then add a fully-formed object to your space — like a door, a sofa, a table, a bed, a car, decor, a pet, or anything else you can dream up.
The interface allows you to change an object’s attributes and functionality, like the color, size, position, or style or what happens when you click it.
The project also takes inspiration from other projects Toff worked on at Google’s AR/VR division, like its VR and AR app-building service Poly (which became another Google causality in 2020), and the 3D modeling tool for VR, Blocks. Rooms’ co-founder Bruno Oliveira also worked on these projects at Google, which is how the two first met. Meanwhile, third co-founder and iOS engineer Nick Kruge, hails from Smule (where he was Director of Product Design) and Uber, in addition to Google, where he worked on YouTube mobile and YouTube Music.
“Basically, I set out for the company to make the digital equivalent of LEGO,” Toff explains. “The thought was, LEGO is one of these few things that kids love, adults love, and adults want their kids to play with,” he says. But LEGO has limitations due to its physical, printed plastic nature. It can be expensive and you can lose parts, for example, Toff noted.
Like a box of LEGOS, Rooms is meant for open-ended play where people use the objects to express themselves in some way — whether that’s building a tiny version of a real-world room, a dream room, or by creating some sort of interactive space, like a simple game or a musical instrument you can click to play, or something else.
The startup seeded its community with 1,000 Voxel 3D objects it commissioned from creators, which can be added and customized in your own space. Every room is also by default public and can be “remixed” — that is, used as a template or jumping-off point for designing your own.

Image Credits: Rooms.xyz
There’s an educational aspect to the software, too, as you don’t only have to interact with the objects via the user interface — you can also click to reveal the code. Rooms uses Lua, the same language that’s used for coding in Roblox. That could help to introduce younger users to coding concepts before moving on to Roblox’s more advanced editing tools.
While the rooms themselves are interactive and can be interconnected with one another, there’s not much more that can be done with them after the design is complete besides share their URL with others to show them off. A “camera mode” lets you take a photo or a smooth dolly shot, but the end result isn’t one-click publishable to social networks. Nor can users create avatars that can move or interact with others, or engage in chats.
“That was an intentional decision — in part, just to keep this as like safe as possible,” Toff explains. “Because as soon as you introduce chat…people can do terrible things,” he says.. Plus, he adds, there’s already too much focus on virtual personas and dressing up avatars and the team wanted wanted to pursue something different.
“For all I know, it could be a huge mistake that we don’t have any of that — and it may make sense to introduce some sort of social experience down the road,” Toff admits. “But for now, it’s all just like just a website or a game you play. It’s all individual.”
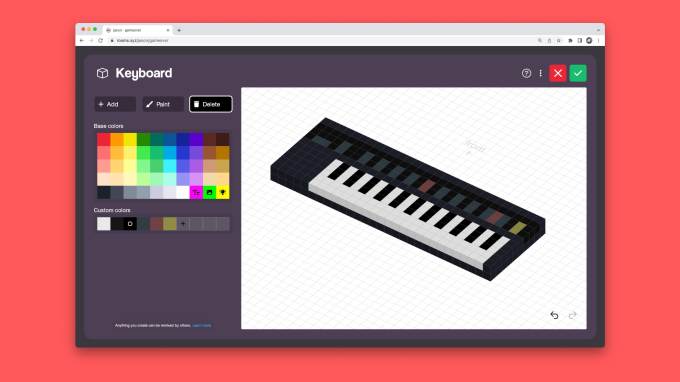
Image Credits: Rooms.xyz
Eventually, Rooms could monetize by selling objects for purchase, subscriptions, or licensing its software for education, but that’s all very much to be determined at this point. As the startup opens up to beta testing, the goal is to see how early adopters use the product and what they end up building or requesting, says Toff.
One area they’re exploring, however, involves the use of ChatGPT. Right now, they’ve created an object of a fortune teller (Zoltar!) which you can pose questions to that are then answered by the OpenAI chatbot, speaking as Zoltar would. Users can copy that code and use it for their own AI-enabled objects, editing the prompt within the code to change the way their object responds.
Also in development is an AI tool that would let users instruct the software to write code for the object they want and how it should behave.
For instance, you could tell it to make your object spin when clicked, and the AI would create the code you need. This functionality is not yet public, however.
The startup — Things Inc. — was founded in 2021, raising $8 million in funding from Andreessen Horowitz (a16z) and $2 million from various angel investors, including Adobe’s Chief Product Office Scott Belsky and Instagram co-founder Mike Krieger, among others. After burning funds too quickly at first, the team downsized their 10-person team to just the three founders in order to maintain enough runway. Now, Rooms.xyz has somewhere around four-plus years, Toff says.
That could allow the company, which has been built via Unity, more time to launch on other platforms. Right now, an iOS app is in development that would serve as a companion for exploring the Rooms built by others. But the team also envisions expanding these creations to the AR/VR platforms from Apple and Meta in the future, too.
“We were like, ‘let’s get this beta out now,’ because once Apple comes out with its [AR/VR device], we’ll see what it does and then we can figure out how to integrate it,” says Toff. ‘All this was built in a way that it could be on a headset very easily,” he adds.
Rooms.xyz is open for beta testing and is free to use.
a16z-backed Rooms.xyz lets you build interactive, 3D rooms and simple games in your browser by Sarah Perez originally published on TechCrunch


