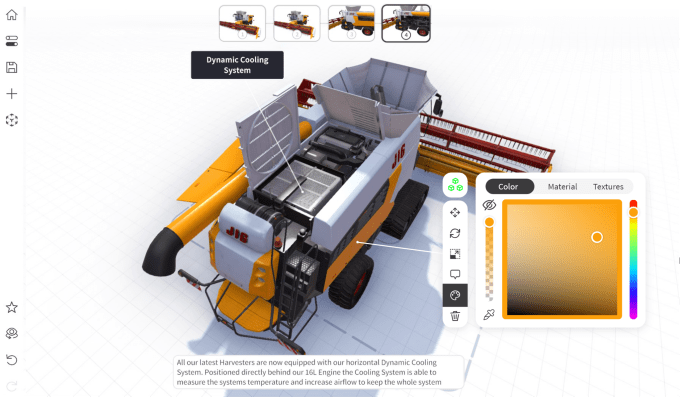
A clutch of startups is trying to topple Adobe’s dominance in three-dimensional modeling and do more than Canva. A freshly funded player is PixCap, which is entering the fray with a no-code, web-based 3D design tool.
Founded in 2020, Singapore-based PixCap just secured $2.8 million from a seed funding round. It was part of the seventh cohort of Surge, Sequoia Capital India and Southeast Asia’s accelerator, which led the round. Cocoon Capital, Entrepreneur First and angel investor Michael Gryseels also participated.
CJ Looi, CEO of PixCap, is building the company when the web experience is undergoing what he called an “evolution from 2D to 3D.” Tech firms from Foodpanda, Alibaba, Shopee, TikTok, Meituan to Lazada have all started to incorporate 3D elements into their logos, ads, and landing pages over the past two years, the founder pointed out in an interview.
These aren’t unique, sophisticated 3D assets developed for movies or video games; rather, they are simple designs like a brand mascot that are reusable across a firm’s marketing campaigns to “enhance user engagement,” suggested Looi, who previously worked on 3D vision and deep learning at robotics startup Dorabot, which is backed by Kai-Fu Lee’s Sinovation Ventures and Jack Ma-founded YF Capital.
“The trend is moving toward interaction,” the founder continued. “The benefit of 3D that 2D doesn’t provide is, in 3D, if you look at most TV ads, a lot of the content uses 3D animation. So something that can be used in your advertisement and your landing pages and apps is far more advantageous to a brand than having 2D somewhere and 3D elsewhere.”
But designers with 3D animation skills are “some of the rarest talents you can find,” observed Cyril Nie, co-founder and CTO at PixCap. Even when creators want to step up their careers by acquiring 3D skills, many are daunted by the complexity of legacy software like Adobe. Gojek spent “close to $200,000 on a branding agency just to create 3D icons for their apps, landing pages and social media,” Looi recalled his recent conversation with an executive from the Southeast Asian ride hailing giant.
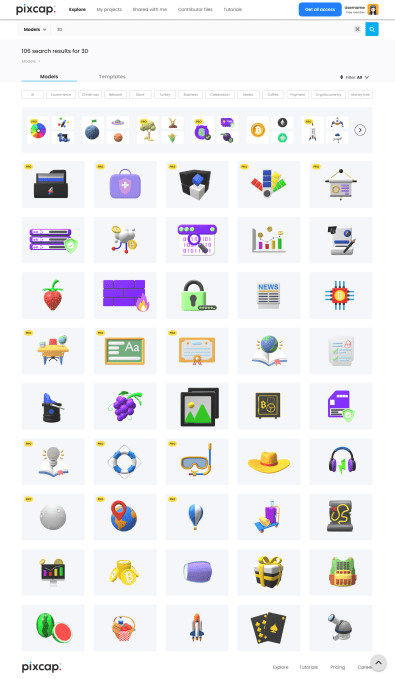
Image: 3D templates from PixCap
The costs of adopting 3D are too prohibitive for most startups. PixCap’s vision is to make the transition to 3D cheaper in the way Canva made 2D designs more accessible. Instead of spending tens of thousands of dollars on hiring a designer for a one-off campaign, marketers can quickly put together a 3D social media graphic on PixCap using its library of templates. With a few clicks, those with no prior 3D knowledge can adjust the lighting and after-effects of objects, rotate them and change the colors to match their brands’ palettes.
The platform has over 30,000 users so far with around a third in North America, followed by top markets like India, Indonesia, and the U.K.
PixCap’s main differentiation from legacy players is its web-based and drag-and-drop interface; compared to younger online solutions, such as Y Combinator-backed Spline, it boasts a greater number of editable templates and “robust” 3D animation capabilities, which Looi argued is the natural next step after static 3D images.
To enhance its moat in templates, PixCap is working on a contributor marketplace that will eventually allow creators to easily sell their works, which will keep the platform replenished with new 3D assets.
Typical of many SaaS startups today, PixCap’s team of 15 members is located across the world — India, Pakistan, the U.K., France and Russia. It plans to spend the proceeds from its new round on global expansion, hiring for its engineering and marketing teams, product development and community building.
Singapore’s PixCap draws $2.8M to power web-based 3D design by Rita Liao originally published on TechCrunch