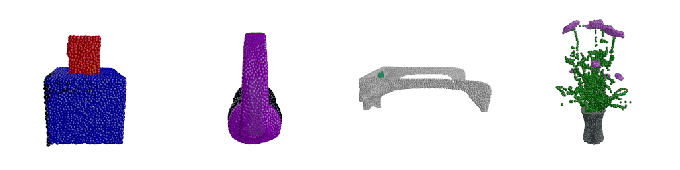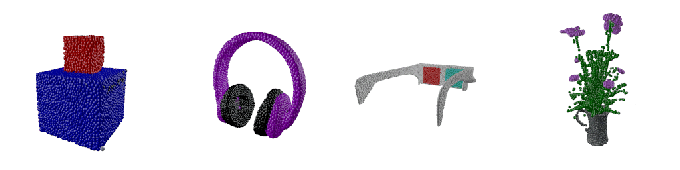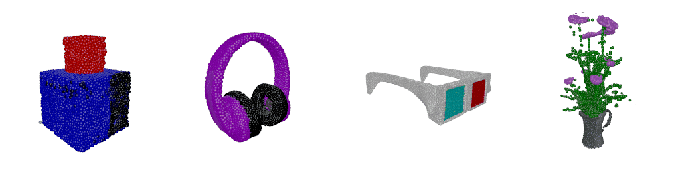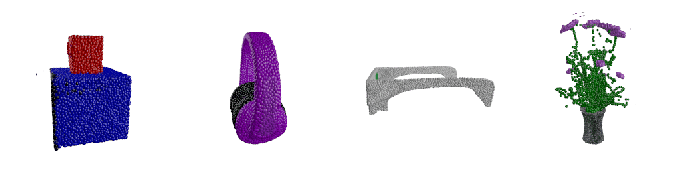
Hexa, a 3D asset visualization and management platform, today announced that it closed a $20.5 million Series A round from Point72 Ventures, Samurai Incubate, Sarona Partners and HTC. CEO and co-founder Yehiel Atias said that the cash will be put toward product development and expanded customer acquisition efforts well into 2023.
HTC’s participation in the round might seem curious. After all, the company was once one of the world’s largest smartphone manufacturers — not exactly entrenched in the 3D modeling space. But HTC’s focus has increasingly shifted over the years from mobile to VR, and it evidently sees Hexa as aligned with its current — and perhaps even future — lines of business.
“The new funding will be used to support our existing customer expansion and keep up with the flow of new customers that are being onboarded. We conducted an early round due to tripling our customer base in 2023,” Atias told TechCrunch in an email interview.
Hexa’s roots can be traced back to 2015, when Atias was working in the retail industry for brands like Walmart and H&M. He — like most people — quickly came to realize that the dressing room experience translated poorly to e-commerce. Atias co-launched Hexa with Ran Buchnik and Jonathan Clark first as a virtual dressing room platform aimed at bridging the massive disconnect. But he later pivoted the business into a general-purpose tech stack for VR, AR and 3D-model-viewing experiences.
“With a combination of AI-powered technology and human artistry, Hexa can help brands and retailers to create, manage and distribute 3D models that can be used for a variety of use cases, including 3D models, AR experiences, lifestyle photos, 360-degree views and promotional videos,” Atias said. “The major value for our client is that they gain the ability to scale quality 3D projects in a short amount of time. They also can manage and assess the impact of their 3D content through our platform.”

Image Credits: Hexa
Lest you think it’s a new idea, there’s an entire cohort of companies out there developing platforms for 3D asset management. Mark Cuban and former Oculus CEO Brendan Iribe recently backed VNTANA, whose product allows users to view shoppable objects in AR and try on items virtually. South Korea’s RECON Labs helps shoppers visualize products by creating 3D models in AR. Emperia helps brands like Bloomingdale’s build shopping experiences in VR. Even Snap’s gotten in the game recently, launching an AR toolkit to turn photos into 3D assets.
So what differentiates Hexa? Atias says it’s the expertise on — and robustness of — its service. Hexa customers can upload an image or have Hexa’s API automatically fetch images from a website. Then the company’s engineers, using AI-assisted tools, create 3D assets and models from the images.
Throughout the process, customers can provide feedback directly on the models, ask questions of Hexa’s engineers and prep the models for use on the web or in AR and VR experiences. Hexa also provides a range of 3D viewer apps for customers to use, including ones for the web and AR, plus code that can be used to insert models into social media posts and video games.
“Since we need to comply with the clients’ server requirements and verify our 3D assets are identical to the source imagery we’ve been provided, a lot of manpower needs to be invested to answer the scale of Hexa’s production,” Clark said via email. “A lot of effort has been done to solve this aspect, as well, and today, Hexa is able to align the 3D asset with the source imagery and thus ensure the asset complies at a pixel and voxel level.”
AR and VR shopping experiences might not have reached most people (at least according to one survey), but Atias believes there’s a large market to be won. Already, he says, 60-employee Hexa has managed to win the business of over 40 brands, including Amazon, Macy’s, Logitech and Crate & Barrel — and raise $27.2 million in total capital.
There might indeed be a growing interest in virtual retail venues, particularly those of the AR variety. Some 48% of respondents to a McKinsey survey said they’re interested in using “metaverse” technology (i.e., AR and VR) to shop in the next five years. In turn, 38% of marketer respondents said they are using AR in 2022, up 15 percentage points from 2017’s 23%.
“Our main competition is animation and graphics studios that use a manual and outdated tech stack,” Atias said. “Much like the gaming industry, the 3D and e-commerce space enjoyed a strong tailwind, becoming a must-have for any organization … Hundreds of millions of users use our technology and engage with our content on a daily basis.”
Hexa raises $20.5M to turn images into 3D objects for VR, AR and more by Kyle Wiggers originally published on TechCrunch