At the same time internet of things (IoT) devices and embedded software are becoming more complex, manufacturers are looking for ways to effectively manage the increasing volume of edge hardware. According to Statista, the number of consumer edge-enabled IoT devices is forecast to grow to almost 6.5 billion by 2030, up from 4 billion in 2020.
Capitalizing on the trends, Memfault, a platform that allows IoT device manufacturers to find issues in their edge products over the cloud, has closed a $24 million Series B funding round led by Stripes with participation from the 5G Open Innovation Lab, Partech and Uncork. The investment brings Memfault’s total raised to more than $35 million following a $8.5 million cash infusion in April 2021.
“We sharpened our go-to-market motion in 2022 and saw a clear acceleration in the business,” Memfault co-founder and CEO François Baldassari told TechCrunch in an email interview. “We feel confident that our playbook for sales-led growth is at a level of maturity where we can double down on our investment and accelerate growth. This was not the case a year ago; there is more talent available on the market than at any time since we started the company.”
Baldassari first conceived of Memfault while at smartwatch startup Pebble, where he worked alongside Memfault’s other two co-founders, Tyler Hoffman and Chris Coleman, for several years. At Pebble, the trio had to investigate hardware issues that were often difficult to fix remotely, which led them to create cloud-based software and performance monitoring infrastructure to improve the process.
After leaving Pebble, François joined Oculus as head of the embedded software team while Hoffman and Coleman took senior engineering roles at Fitbit. The infrastructure they created at Pebble stuck with them, though, and in 2018, the three reunited to found Memfault.
“We offer the tools to de-risk launch, prepare for the inevitability of post-launch issues and deliver a continuously improving, higher-quality product overall,” François said. “We can help companies ship more feature-rich products with continuous feature updates after the devices are in the field while helping companies stay in compliance with environmental, privacy and security regulations and avoid service-level agreement and warranty violations.”
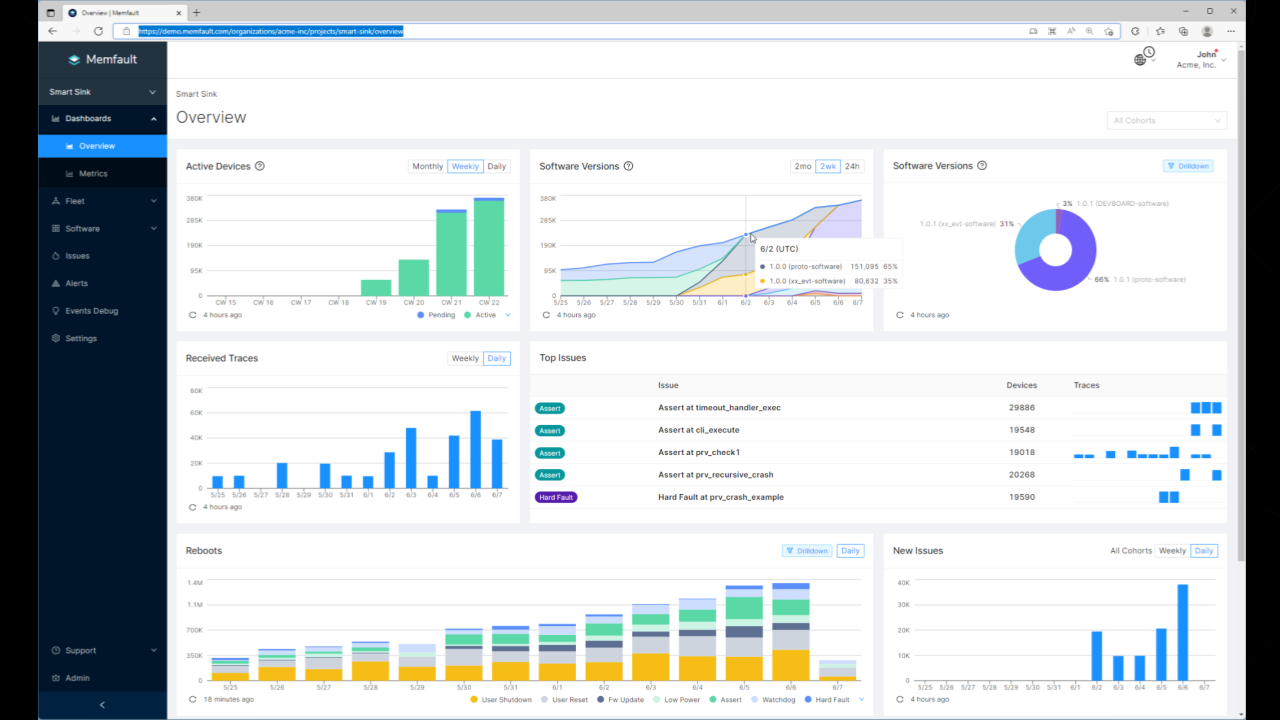
Image Credits: Memfault
Stripping away the marketing fluff, Memfault provides software development kits (SDK) that let manufacturers upload performance data and error reports to a private cloud. There, it’s stored, analyzed and indexed so engineers can access it via a web interface to look for anomalies and troubleshoot problems as they occur.
François acknowledged that some manufacturers try to extend software reliability tools to cover hardware or build in-house teams to tackle bugs. But he argues that both approaches end up being more expensive and require more technical resources than deploying a service like Memfault.
“You can never anticipate every use case that a user might subject your device to, and there are some bugs that only surface in one in 10,000 instances. Trying to replicate that is nearly impossible,” François said. “Using Memfault, engineers react to issues in minutes rather than weeks, the majority of issues are automatically deduplicated and a clear picture of fleet health can be established at all times.”
While cybersecurity isn’t its main focus, Memfault has sometime rivals in startups like Sternum, Armis Shield-IoT and SecuriThings, whose platforms offer remote tools for monitoring security threats across IoT device fleets. More directly, Memfault competes with Amazon’s AWS IoT Device Management, Microsoft’s Azure IoT Edge, Google’s Cloud IoT and startups like Balena and Zededa, which sell utilities to seed over-the-air updates and perform high-level troubleshooting.
Memfault claims to have a sizeable market foothold regardless, with “hundreds” of companies in its customer base including Bose, Logitech, Lyft and Traeger. And it’s not resting on its laurels.
To stay ahead of the pack, Memfault plans to use the proceeds from its Series B to expand its platform’s software support (it recently announced Android and Linux SDKs) and invest in out-of-the-box integrations, adding to its existing partnerships with semiconductor manufacturers including Infineon, Nordic Semiconductors and NXP. Memfault also intends to expand its headcount, aiming to roughly double in size from 38 people to 80 by the end of the year.
François said that Memfault is also exploring ways it could build AI into future products, although that work remains in the early stages.
“We see promise in AI’s ability to help us develop sharper anomaly detection and error classification capabilities,” François said. “We’ve accumulated the largest corpus of hardware and firmware errors in the industry and hope to train AI systems on that data in the future.”
Asked about macroeconomic headwinds, François — who wouldn’t discuss revenue — admitted that the pandemic-spurred chip shortage affected Memfault’s customers and market “quite a bit.” But it turned out to be an blessing in disguise.
“In some cases, customers have been unable to find enough chips to produce the number of devices they planned on. In other cases, they’ve had to switch to new chips they’ve not previously had on their devices,” François explained. “In these cases, Memfault has been a huge help to our customers. Many engineers tell us that they aren’t sure what their firmware will look like running on these ‘Frankenstein’ devices — but with visibility into fleet data, diagnostics and debugging info from Memfault, they’ve been able to ship confidently.”
François volunteered that Memfault has maintained “high” gross margins and a low burn multiple — “burn multiple” referring to how much the company’s spending in order to generate each incremental dollar of annual recurring revenue. (The lower the multiple, the better.) Of course, it’s all tough to evaluate without firmer numbers. But when pressed, François stressed that Memfault hasn’t been growing at any cost.
“We’ve always been focused on building a long-term sustainable business,” François said. “Although there is a broader slowdown in tech, the global trend is going towards more automation. Most customers and prospects have told us how they are willing to spend on software and automation to stay ahead of competition.”
Memfault raises $24M to help companies manage their growing IoT device fleets by Kyle Wiggers originally published on TechCrunch